The Billion-Dollar Opportunity That Is Aurangabad Industrial City (AURIC)
There is a recognisable uptick in the ease of doing business in India as well as in the perception of the same in global markets; and the current administration continues to proactively work to build upon this further. To develop this mandate, various ministries and specially created teams have aligned to create futuristic, country-wide pro-business infrastructure and policies.
The vision and commitment of the Indian Government to grow the Indian economy to USD 5 trillion by 2025 has taken shape not only in the form of pro-business policies but also in that of several large-scale infrastructure projects to boost industrial development. The Delhi Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC) is one such project.
The Delhi Mumbai Industrial Corridor
Being developed as an industrial zone spanning across the 6 Indian states of Maharashtra, Delhi-NCR, Haryana, Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Uttar Pradesh, the entire stretch expands to nearly 1500 km, and will leverage the logistical support and connectivity provided by a Dedicated Freight Corridor (DFC) connecting the Delhi-NCR to the JNPT and MBPT ports of Mumbai.
The DMIC is India’s most ambitious and one of the world’s largest infrastructure projects that is propositioned to become India’s new global manufacturing and trading hub. As part of the project, smart cities are being created along the corridor wherein the manufacturing setups and infrastructure developed will include Industry 4.0 technologies. The goal of DMIC is to expand India’s manufacturing and service base, consequently making it India’s primary global trading hub. And to ensure that the project attains fruition in the most beneficial and sustainable ways possible, 24 investment regions have been planned along the corridor – Aurangabad Industrial City (AURIC) is one of these zones.
Aurangabad Industrial City – Everything You Need To Know
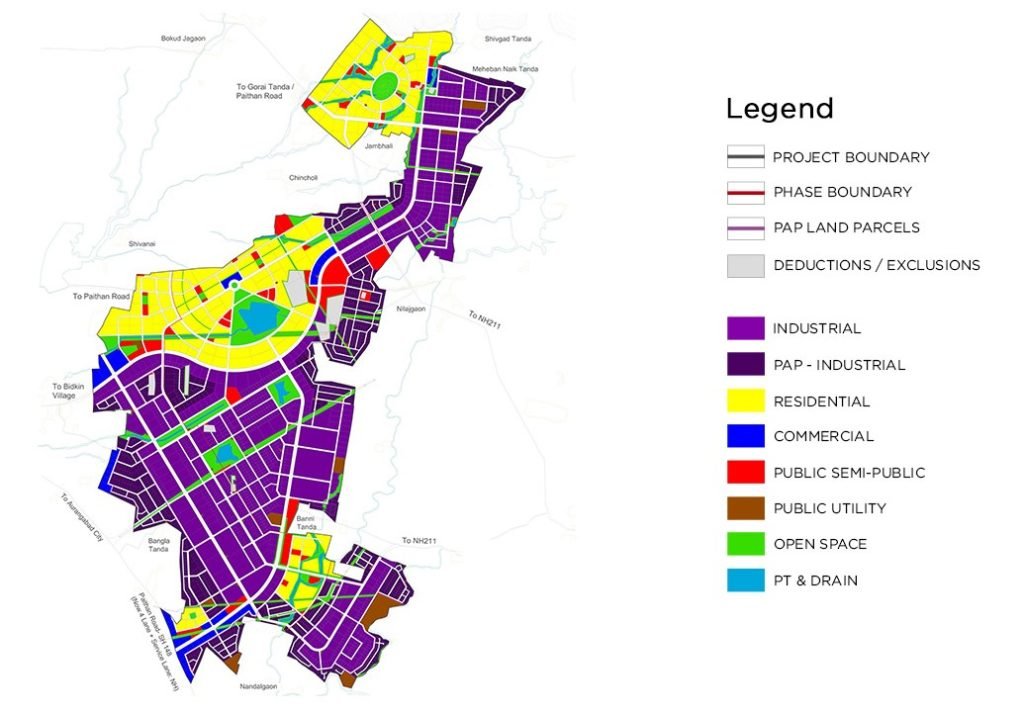
Spread over a total area of 10000 acres (~40 km2), Aurangabad Industrial City (AURIC) can surely be considered as India’s most well-planned smart industrial city project that is being developed by Aurangabad Industrial Township Limited (AITL). AITL is a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) that has been created between the DMIC Development Corporation (DMICDC) and the Maharashtra Industrial Development Corporation (MIDC).
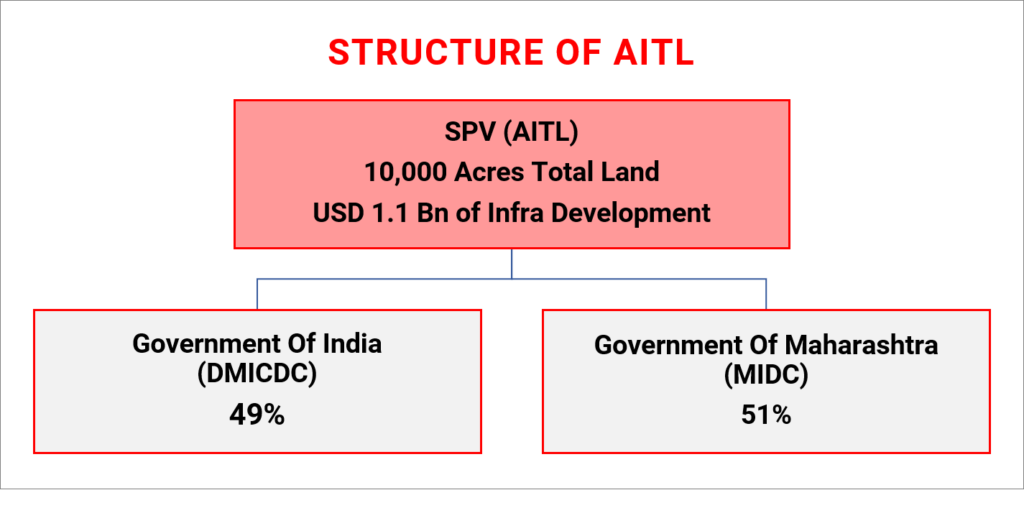
The entire development and management of AURIC is being undertaken by AITL, wherein the latter has not only determined its own set of Development Control Regulations (DCR) but is also acting as the single point of contact for building permissions, utilities connections, and all related infrastructure provisions. Additionally, AITL will be solely responsible for the day-to-day management of the industrial township after completion; and has its base of operations from the state-of-the-art and fully functional Admin Block building.
Below are some key statistics that capture the scale and potential of the project:
- An infrastructure budget of USD 1.1 Billion has been approved by the Government of India, and major contributions are already in effect
- As a manufacturing hub, the zone is expected to output with an export value of nearly USD 11.6 Billion
- The extensive industrial development will result in the creation of over 300,000 new jobs across employment categories
- Targeting a resident population of approximately 500,000, the city is being developed fully equipped with world-class social amenities to make it a holistic ecosystem
Connectivity To Aurangabad Industrial City
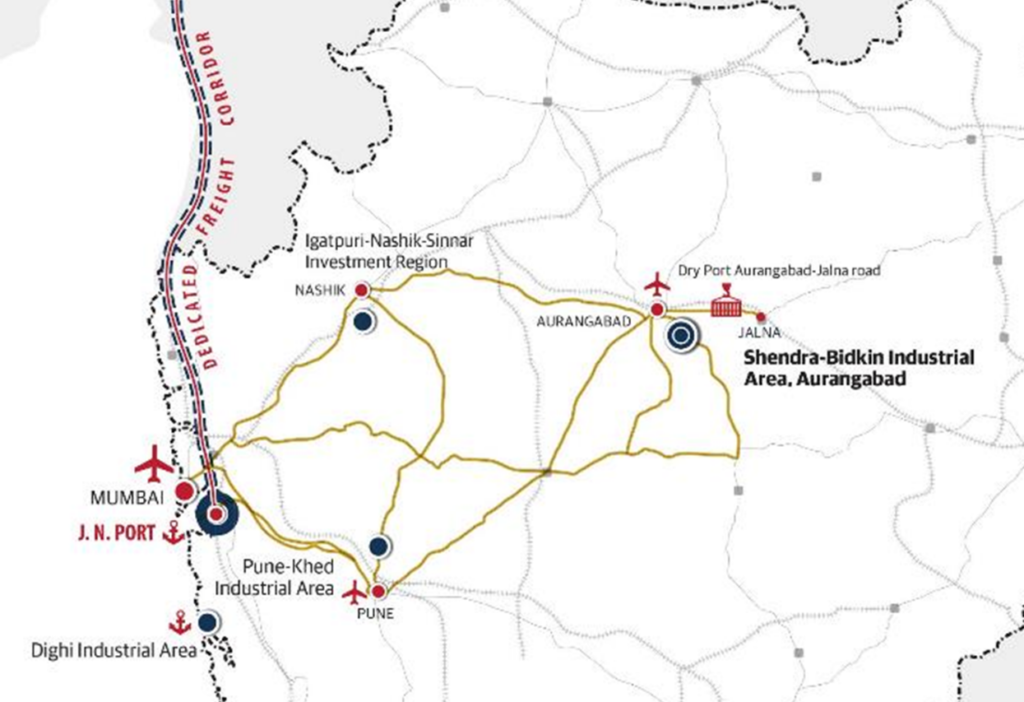
Aside from its proximity to the city of Aurangabad, which is connected globally through its international airport, AURIC is connected by 3 National Highways and 4 State Highways. More importantly, the dry port of Jalna (which is managed by JNPT, India’s largest seaport) is less than 40 km from the new industrial hub, thus enabling AURIC with widespread logistical connectivity.
Ease Of Doing Business In AURIC
The reason why Aurangabad Industrial City stands apart from most other industrial parks or Special Economic Zones (SEZs) in India, is because it has been modelled specifically to execute the Government’s mandate of increasing the ease of doing business in India.
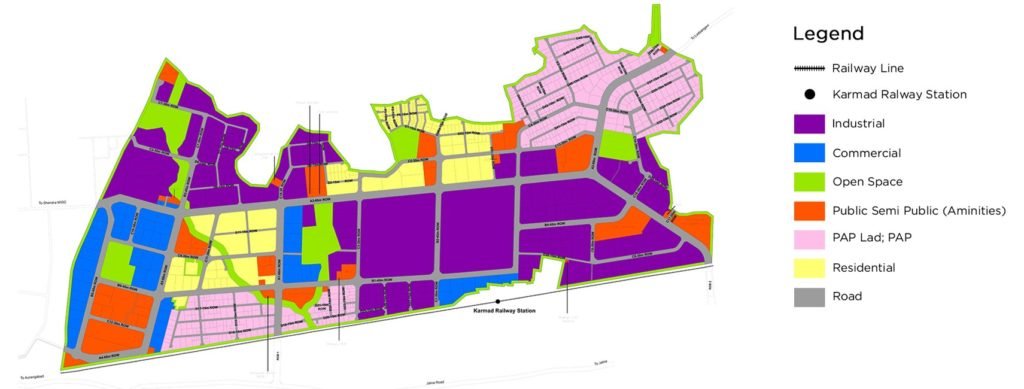
The industrial city has been planned in a manner that 60% of its area is allocated for industrial zones and 40% is designated for offices, residences, retail outlets, hospitals, schools, parks, entertainment hubs, and so on.
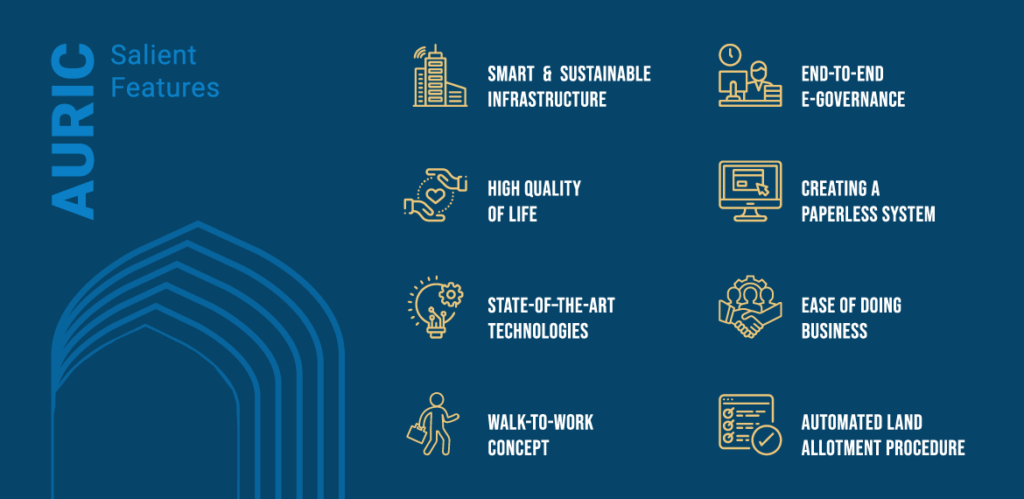
More importantly, the city is being built for the future through the development of high-value, sustainable infrastructure that will support long-term economic vitality, a high quality of life, and a knowledge-based ecosystem with breakthrough innovation and efficiency. Adopting state-of-the-art technologies, the infrastructure set up will focus on clean, reusable, and recycling methodologies, and industrial growth will be encouraged in targeted areas to build upon the industrial success of the region.
Project Phases: Shendra And Bidkin
The entire project has been divided into two phases basis two regions of development:
Phase 1 – SHENDRA
Having a total area of 8.39 km2, this region lies near the village of Shendra which is only 17 km from Aurangabad city. Acting as a prototype of the project, all issues identified in the development of the infrastructure of this zone are being weaned out for the successful setup of Phase II.
Phase 2 – BIDKIN
With a total area of 31.79 km2, Bidkin is the major phase of the AURIC project. The infrastructure of this phase is in full development and is at the stage wherein companies and investors who are interested to setup their manufacturing units in India, can connect with AITL through the website.
But Why Specifically AURIC?
There are several Special Economic Zones (SEZs) and Industrial zones existing as well as being developed across India, wherein investors do stand to gain from tax benefits and relaxations. However, AURIC is more than just that.
As mentioned earlier, as a project AURIC has been developed to help companies not only setup their manufacturing units with ease but also run their operations in a hassle-free manner. To make this possible, AITL has implemented several initiatives for the following:
Ease Of Setup
- Investors who are interested to setup their unit at AURIC can apply and track their applications online
- For sake of convenience as well as transparency, simplified payment options have been put in place and can be undertaken through the payment gateway
- Applicants will be kept updated about the status of their applications through automated SMS and email notifications
- For all concerns, queries, and assistance, AITL has instrumented a helpdesk to provide support to all interested parties
- Offer letter system has been opted out
- AITL is doing final lease which ensures that no other parties or middlemen are involved, and that no lease agreements will be required; as well as the offer letter system has been opted out
- All plots available to investors will be accessible on the online Geographic Information System (GIS) on GIS system
- To ensure there is easy access to information, plot history sheet-property cards are made available
Ease Of Operations
- AITL is the special planning authority for the project therefore centralizing governance and management of the project, as well as providing single window clearance for all matters related to the project
- Plug-and-play design for the infrastructure makes utilities available at doorstep, with AITL providing for utility connection permissions; all of which will be undertaking online
- Power supply is be available 24×7; and will be managed and distributed by AITL
- 42% of the water demand is met through recycled water from the water treatment plants equipped with state-of-the-art with SCADA controls
- Walk-to-work concept ensures that people employed at the city can commute easily between work and residence, thus positively impacting the overall living experience for AURIC
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) clearance has been obtained for all industries from the Ministry of Environment and Forests (MOEF), thus avoiding any future roadblocks or issues
Of course, aside from the above, there do exist the obvious financial benefits in the form of tax incentives and reimbursements, and the extent of which are determined by the amount of investment being made by a company.
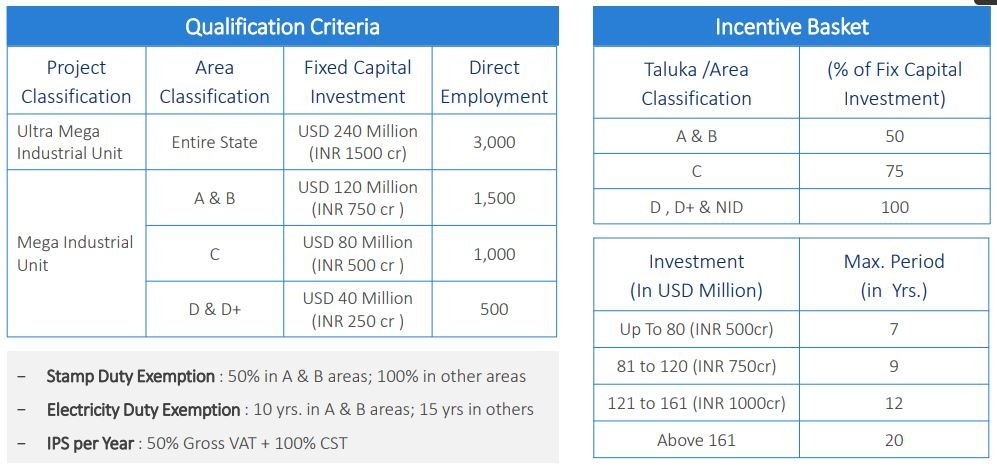
Although the project is jointly run by the DMICDC and MIDC bodies, it comes under the guidelines prescribed by the Maharashtra Industrial Policy, on account of its geographical location. According to this policy, the qualification criteria applicable to business is defined by the size of the investment being made, and hence the category they are tagged with. Consequently, the benefits available to investors differs based on their respective categories.
Read More On The Brief: Inland Waterways In India: A 10,000 Kilometer Opportunity
Qualification Criteria For Benefits In AURIC
As per the Industrial Policy, AURIC is classified as a D & D+ project; and the details of its relevant eligibility criteria and related benefits are highlighted in the table below:
Incentives Available For Investing In AURIC
In addition to providing the above mentioned operational, administrative, and financial benefits to investors, AITL has worked to ensure that there exists a holistic solution to enable the ease of doing business at AURIC. Some of this are listed below:
Industrial Policy – Fiscal Support
- Industrial Promotion Subsidy (IPS) in form of ‘Gross SGST’ Abatement
- Stamp Duty Exemption
- Electricity Duty Exemption
- Power Tariff Subsidy
- State Equity Participation
Industrial Policy – Non-fiscal Support
- Skill Development
- Single Window Clearance (SWC)
- Investor Facilitation
- Investor After Care Cell
Special Incentives
- 20% additional incentives for Food Processing Units, Agro-processing Units and Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs)
- Additional incentives for Thrust Sectors, Green Energy and Industry 4.0-based units
Sector & Region-Specific Incentives
- Capital Subsidy – Textiles, Electronics System Development and Maintenance (ESDM) & Semiconductor Wafer Fabrication (FAB), Information Technology (IT) / IT-enabled Services (ITeS)
- Sector Development Fund – ESDM, Textile, Start-ups
- Interest Subsidy Scheme – ESDM & FAB
- Critical Infrastructure Fund – IT/ITES
- Power Subsidy – ESDM, Food, Textile, Marathwada, Vidarbha
Policy Highlights
- 100% Captive Process Vendor (CPV) investment can also considered as part of Fixed Capital Investment (FCI)
- Projects of Special Importance (may or may not be Mega/Ultra-Mega projects) may be considered for customized package of incentives on case-to-case basis
- State government shall be an equity partner (in the form of shares only of 9%) through Maharashtra Vikrikar Rokhe Pradhikaran Limited (MVRPL) in LSI, Mega, Ultra-Mega industries with FCI of more than USD 70 m
- Allocation of MIDC land to Mega and Ultra-Mega projects on priority basis
Addressing The Key Challenges Of Current Times
The current administration is aggressively pursuing its agenda of economic and industrial development. To make this happen, there is the explicit need for better infrastructure along with supportive policies. At this stage, creating a platform keeping the next 4-5 decades (at the maximum) in mind as a time frame is plausible.
And for exactly this reason, AURIC has been envisioned and planned for the future, For this world-class standards in civil planning and construction have been adopted at AURIC; and to ensure that this infrastructure is easily accessible and managed, AITL has developed the same through underground trunk infrastructure, with nodes for door-step connectivity for each land-plot.
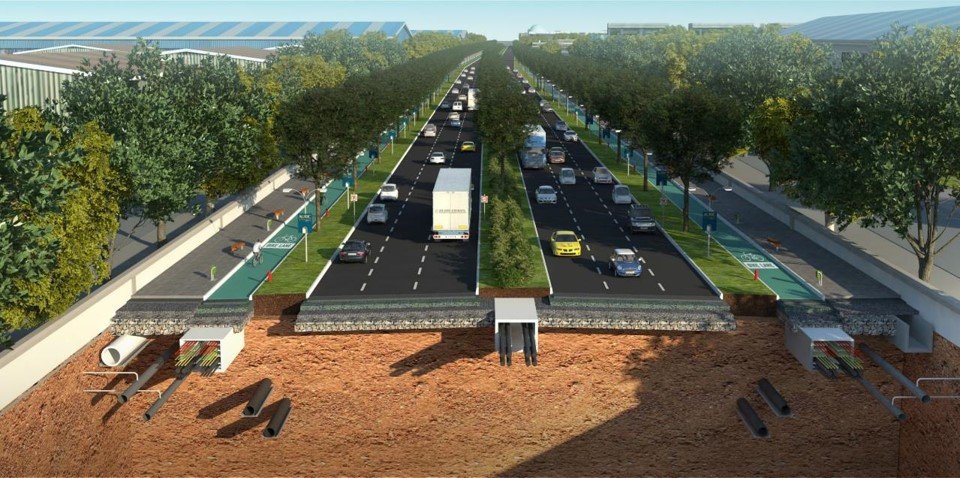

Infrastructure and Technologies
-
Water
- Diversifying sources – fresh water, recycled water (Demand: 116 MLD)
- 42% water demand through recycled water
- All treatment plants to be state of art with SCADA Controls
- Flow meters for flow measurement, water accounting and operational efficiency
-
Power
- Underground electrical distribution lines
- Gas Insulated Switchgear – Compact design and Minimizes power losses
- SCADA control and feedback to IOC
- Reduced downtime
- Two sources of power supply to substations in AURIC
-
Information and Communications Technology (ICT)
- City-wide Wi-Fi services
- E-Governance systems
- Mobile app-based services
- Multi-service digital kiosks for public information
- Digital wayfinding and maps
Solid Waste Management
- Estimated solid waste generation – 250 megaton
- Segregation at source for bio-degradable wet and non-biodegradable dry solid wastes
- Processing of biodegradable waste in the bio-methanation plant
- A scientific sanitary landfill is proposed within the project area for disposal of inerts and other rejects
- Maximum efforts will be made to divert wastes from reaching the landfill by adopting waste management strategies: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
Invest In The Future, For The Future
For companies with manufacturing-based businesses who are planning to incorporate or expand their operations in India, projects such as AURIC present unique opportunities to not only setup but also leverage the ecosystem. In addition, there also exists the opportunity for companies to capitalize on the incentives provided through Industrial Policies, the Make In India programme, and the fiscal boost being extended to companies through tax benefits and relaxations.
In particular, investing into projects such as AURIC enables companies to plan and work into the future rather than only utilizing existing industrial infrastructure and remaining limited in terms of expansion.
To explore this opportunity for growth, which is not only wider but also more potent, interested companies can connect with AITL directly from its website.
About The Author

